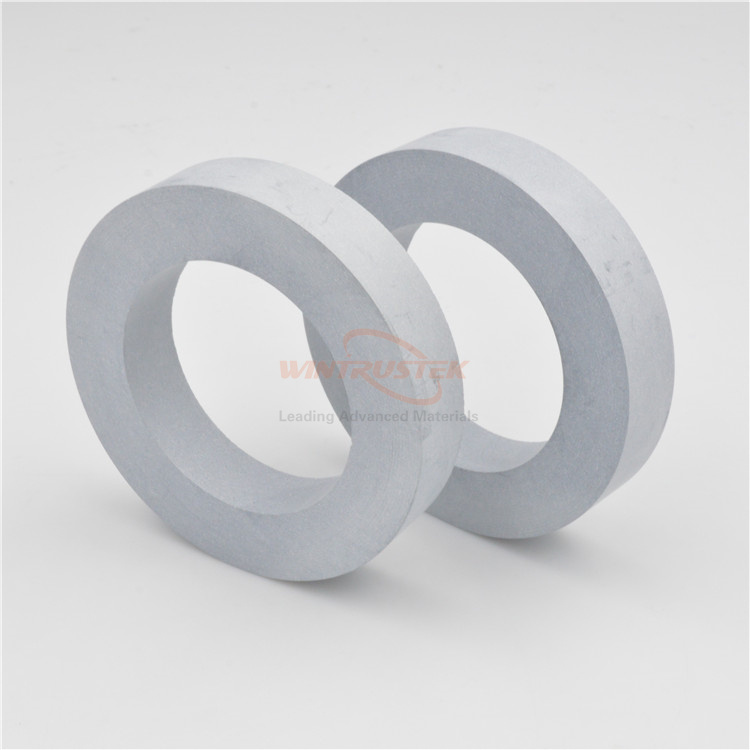
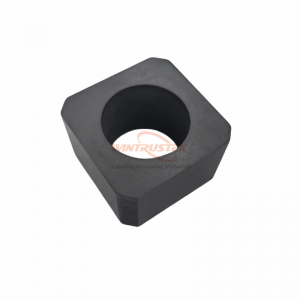
(SNBN Breaking Ring Produced by Wintrustek)
Horizontal continuous casting requires moving molten material from the holding crucible to the graphite die and cooler assembly without using gravity. After going through a graphite die and several holding components, the molten material finally passes through a refractory ring called the break ring to enter the solidification zone. It is crucial that the break ring retain its integrity during the sudden temperature change that occurs when the hot zone gives way to the cold zone (solidification zone). It must allow the molten substance to keep flowing freely without clinging to or building up at the intersection. Break rings are an essential component of horizontal continuous casting, even though they appear to be a straightforward component of the complete assembly. The entire heat would be lost in the event that these parts failed or broke, posing safety risks and requiring a large amount of downtime for part replacement and cleanup.
Boron nitride exhibits outstanding high-temperature resistance, electrical insulation, and thermal conductivity. At 1800°C, it exhibits outstanding chemical stability and remains stable against carbon and carbon monoxide. Furthermore, molten metal, molten salt, and non-oxide slag do not corrode it. Additionally, BN may be produced into high-precision pieces and is machinable. The horizontal continuous casting separation ring of molten steel has made extensive use of boron nitride rings. In an atmosphere with high vacuum, it can continue to lubricate while withstanding high temperatures.
Boron Nitride Ring Advantages
Low metal molten wettability
Low thermal expansion and comparatively strong thermal conductivity
A comparatively excellent resilience to heat shock
Extremely high operating temperature with appropriate protection against inert gases
BN Ceramic has many composites types, SNBN performs the best in the horizontal continuous casting equipment:
When it comes to the horizontal continuous casting of nonferrous metals, SNBN (boron nitride+silicon nitride) composite ceramics perform exceptionally well. The rings are perfect for guaranteeing a steady and clear separation during metal flow since they are non-wetting to molten metal, oxidation-resistant, and chemically inert.
Advantages of SNBN Breaking Ring
Oxidation resistant: up to 1000°C in air
High-temp stable: in vacuum or inert gas, up to 1700–1800°C
Non-wetting: prevents slag and metal from adhering
Erosion and corrosion: withstands reactive metals and is resistant
The Advantages of the SNBN Breaking Ring Compared to the Graphite Ring
SNBN ceramic breaking rings, which are designed for rigorous casting processes, perform better than graphite rings because they are completely free from carbon contamination and have remarkable oxidation resistance. Their non-wetting surface and robust structure under heat cycling guarantee superior casting finishes and smooth molten metal flow.
Typical Applications
Continuous horizontal casting systems for nonferrous metals
Ceramic barriers for molten copper, nickel, and aluminum alloys
Graphite ring replacement in metal separation control
Oxidation-resistant components for high-temperature metal processing