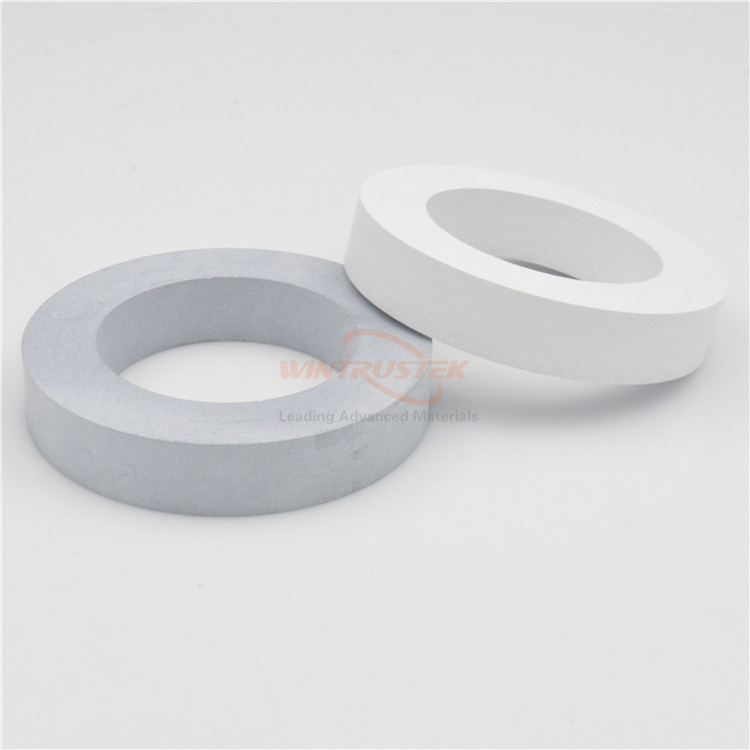
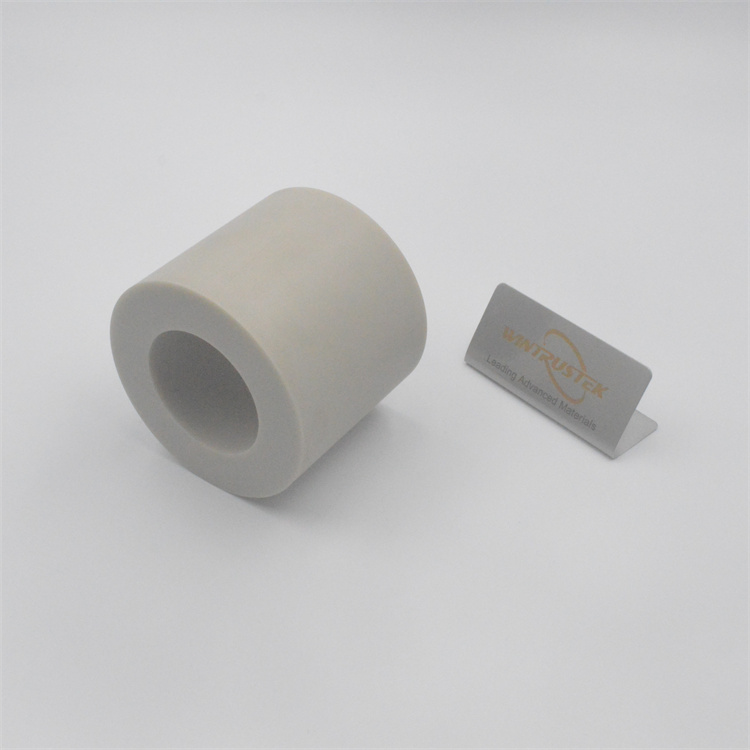
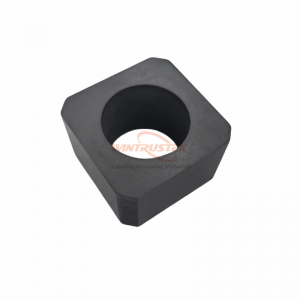
(BN Horizontal Continuous Casting Ring Produced by Wintrustek)
Boron nitride is perfect for a range of molten metal contact applications because of its exceptional thermal shock resistance and superior chemical resistance against the great majority of molten metals. A further benefit of boron nitride over conventional ceramics is its ease of machining into intricate shapes for rapid prototyping.
Melted metal flowing continuously into a mold is known as continuous casting. The molten metal then solidifies into a continuous length. This process is intended to create metal products like slabs, billets, and beams in large quantities with consistent cross sections. The continuous casting procedure commences with the melting of metal, which is subsequently poured into a water-cooled mold. The metal is solid but still malleable as it departs the mold. This enables it to be shaped into lengthy sections without interrupting the casting process.
Continuous casting offers numerous benefits. It provides a high level of automation, which minimizes human error and reduces labor costs. Continuous casting is also remarkably effective, as it enables:
Industries that necessitate substantial quantities of standard geometries are particularly well-suited to continuous casting. This encompasses the construction and automotive manufacturing industries, where the demand for beams and slabs is both consistent and substantial.
The process of casting metals, whether in their pure or alloyed form, entails the transfer of molten metals into pre-prepared die forms. To guarantee process consistency, productivity, and efficiency, it is necessary to optimize the process conditions in terms of temperature, alloying constituents, and component geometry.
When employing various continuous casting and direct casting molds to produce the ideal metal shape, there are numerous variables to evaluate. The quality of the ultimate product may be influenced by the material of the cast, such as metal or ceramic. Manufacturers must evaluate whether the material will exhibit defects or react to thermal expansion.
Boron nitride offers an optimal solution, whether in the form of sintered components or when applied in liquid form to create a boron nitride surface coating.The high release properties of boron nitride prevent the slurry and its oxides from adhering to the surface.Therefore, it is feasible to enhance the casting process's productivity.
In metal casting applications, boron nitride has shown great effectiveness, especially in continuous casting. Break rings, a transitional element between the hot and cool zones of a continuous casting line, are made from hot-pressed boron nitride ceramics that have been machined. This is an important but frequently disregarded step in the casting process. The melt must be able to pass through the break ring and into the solidification zone without adhering. It must also be able to tolerate extreme temperature changes. Break ring failure can be quite expensive. For this reason, materials with low friction coefficients and strong thermal shock resistance are perfect. BN are excellent in this field.