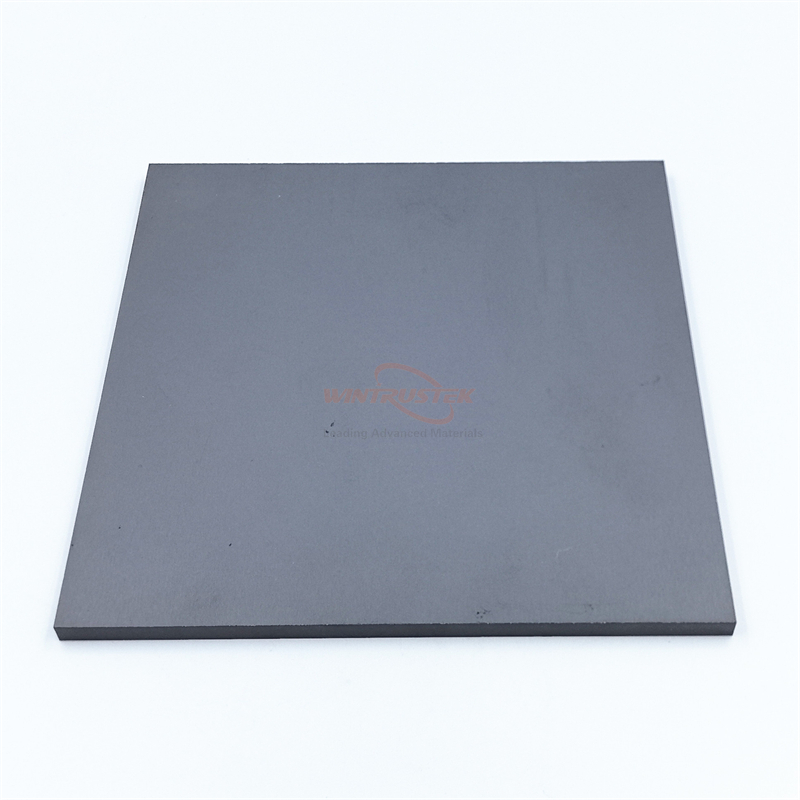
(Hot-pressed AlN Produced by Wintrustek)
Aluminum nitride (AIN) is renowned for its excellent thermal conductivity and exceptional electrical insulating qualities. It is a common ceramic substance used in a wide range of electrical equipment. Aluminum nitride ceramics are resistant to molten metals, including copper, lithium, and aluminum, in addition to their thermal expansion and electrical insulating properties. Aluminum nitride is a useful material in various industrial applications due to its chemical and physical properties.
However, in manufacturing, aluminum nitride is primarily separated into two types based on the sintering process: pressureless sintered aluminum nitride and hot-pressed aluminum nitride. The features and applications of these two categories differ significantly.
Pressureless aluminum nitride mixes high-purity aluminum nitride powder with a small amount of a sintering aid (such as Y2O3), shaping the mixture into the desired form (for example, by dry pressing or isostatic pressing), and then sintering it at a high temperature (1800°C to 2000°C) under a protective inert atmosphere (nitrogen). This process relies on the reaction between the sintering aid and the alumina present on the surface of the AlN particles, forming a liquid phase that promotes the rearrangement and densification of the particles.
Features:
Lower cost: the equipment requirements are relatively simple, making it suitable for large-scale mass production.
Complex shapes: it can manufacture various irregularly shaped parts and thin plates (such as ceramic substrates).
Performance: although it can meet most industrial needs, due to the lack of external pressure, tiny pores are easily present in the material, and the density is usually between 97% and 99%.
Main Applications:
Semiconductor packaging substrates (such as LED and power module substrates)
Heat sinks and insulating gaskets
Corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant device components
Hot-pressed aluminum nitride is produced using a special process called hot pressing. During high-temperature sintering, a unidirectional high pressure of tens or even hundreds of megapascals is applied to the material. This synergistic effect of high temperature and high pressure is key to achieving its exceptional performance.
Features:
Extremely high density: pressure forces out the pores between particles, resulting in a density that can approach the theoretical value (>99%).
Excellent mechanical properties: compared to conventionally sintered AlN, hot-pressed AlN has higher flexural strength and hardness.
Excellent thermal conductivity: due to the extremely low porosity, phonon scattering is reduced, and its thermal conductivity is usually more stable and closer to the upper limit.
Limitations: high cost, low production efficiency, and typically only simple geometric shapes such as discs or blocks can be processed.
Main applications (high-end specialized requirements):
Heat dissipation and packaging of high-power lasers
Next-generation high-power density radio frequency/microwave devices
Heat dissipation for ultra-high reliability electronic systems in the aerospace field
Scientific research equipment or benchmark testing components under certain extreme conditions
How should you choose?
Choose pressureless aluminum nitride if: You are working with electronic circuit boards (PCBs), LED heat sinks, or simple industrial insulation components. Pressureless aluminum nitride is the most cost-effective and mature option.
Choose hot-pressed aluminum nitride if: Your application environment is extremely demanding, such as electrostatic chucks (ESCs) for semiconductor etching equipment, high-performance laser bases, or precision structural components that need to withstand high mechanical stress. The density and strength advantages of hot-pressed aluminum nitride are irreplaceable in these cases.