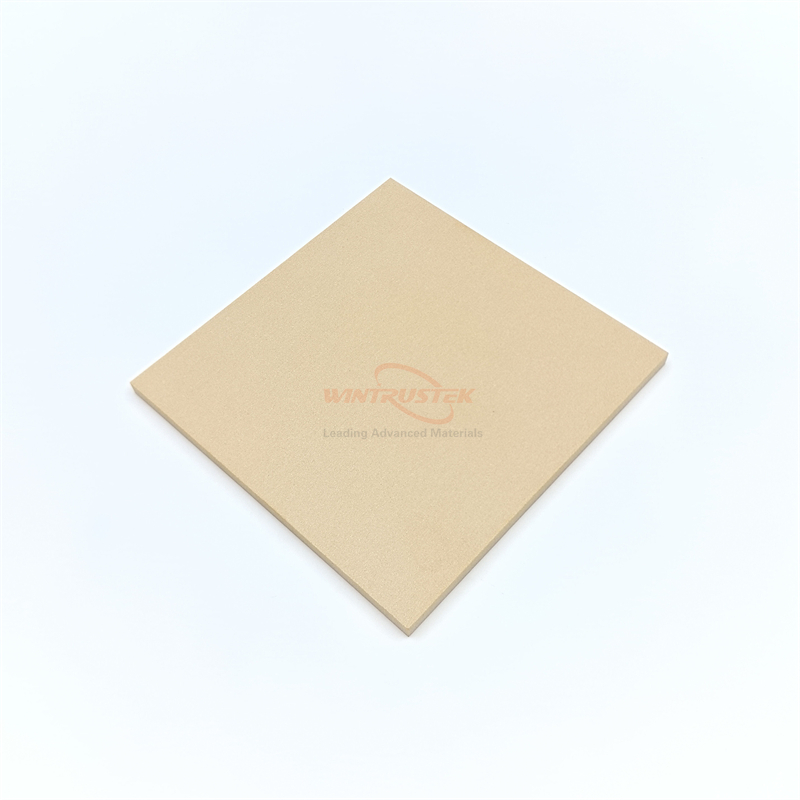
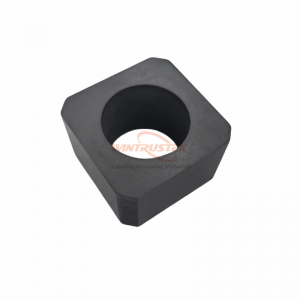
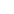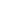(Magnesia-Stabilized Zirconia Sintered Plate Produced by Wintrustek)
Zirconia is available in numerous grades, the most popular of which are yttria partially stabilized zirconia (Y-PSZ) and magnesia partially stabilized zirconia (Mg-PSZ). Both of these materials possess exceptional qualities. Depending on the operating environment and design, specific grades may be appropriate for certain applications.
Magnesia-stabilized zirconia incorporates magnesium oxide as a stabilizer into zirconium oxide, allowing it to maintain a more stable phase structure at high temperatures. It has good ionic conductivity and chemical inertness at high temperatures. It is widely used in industries like metallurgy, energy generation, and advanced sensors. In metallurgy, it is critical for producing long-lasting components for molten metal handling and high-temperature crucibles. This material is used in the energy sector for solid oxide fuel cells and oxygen sensors. In sophisticated sensor applications, it is an important material for gas analysis and lambda probes in automobile exhaust systems. Magnesia-stabilized zirconia sheets are used in emerging technologies such as thermal barrier coatings for gas turbines and ceramic membranes for hydrogen production.
Let's see the advantages and applications of magnesia-stabilized zirconia sintered plate.
Advantages:
Low Thermal Conductivity: Improves energy efficiency in thermal insulation applications.
High Thermal Shock Resistance: Maintains integrity during fast temperature variations.
Chemically stable: resistant to corrosion by acids, alkalis, and molten metals.
Superior mechanical strength: Provides longevity and load-bearing capacity at high temperatures.
Long Service Life: Can withstand extreme situations with minimal damage.
Applications:
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs): Serve as an insulator and structural element.
High-temperature kiln furniture: used in sintering furnaces as setters, plates, and supports.
Metal casting and foundry: Used in the processing of non-ferrous metals as crucibles or liners.
Steel and Glass Industry Refractory Parts: Able to withstand heat cycling and aggressive slag.
Thermal Barrier Systems: Used as insulating layers in reactors and industrial furnaces.
Compared to Alumina and SiC Sintered Plate:
When it comes to sintered plates, magnesia-stabilized zirconia is regarded as a high-end option due to its great overall performance. Compared to alumina sintered plates, which are lower in cost but offer limited strength and a higher risk of reaction, or silicon carbide sintered plates, which lack sufficient stability in oxidizing atmospheres, magnesia-stabilized zirconia provides irreplaceable advantages. It combines superior thermal shock resistance, high mechanical strength, and excellent chemical inertness, ensuring that precision electronic components remain uncontaminated and secure during the sintering process.